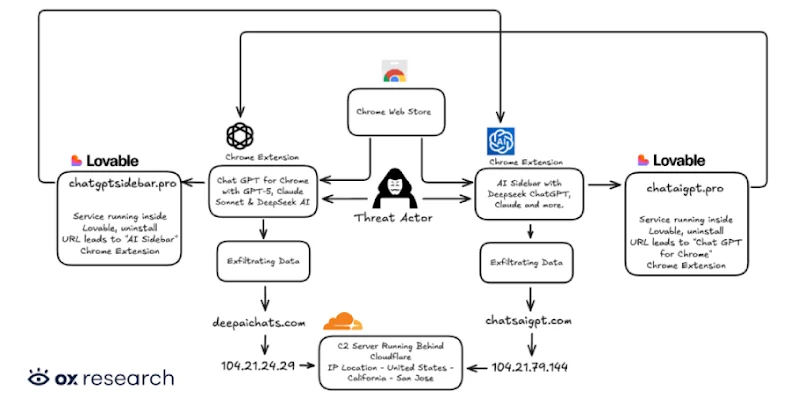
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered two new malicious extensions on the Chrome Web Store that are designed to exfiltrate OpenAI ChatGPT and DeepSeek conversations alongside browsing data to servers under the attackers’ control.
The names of the extensions, which collectively have over 900,000 users, are below –
- Chat GPT for Chrome with GPT-5, Claude Sonnet & DeepSeek AI (ID: fnmihdojmnkclgjpcoonokmkhjpjechg, 600,000 users)
- AI Sidebar with Deepseek, ChatGPT, Claude, and more. (ID: inhcgfpbfdjbjogdfjbclgolkmhnooop, 300,000 users)
The findings come weeks after Urban VPN Proxy, another extension with millions of installations on Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge, was caught spying on users’ chats with artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots. This tactic of using browser extensions to stealthily capture AI conversations has been codenamed Prompt Poaching by Secure Annex.
The two newly identified extensions “were found exfiltrating user conversations and all Chrome tab URLs to a remote C2 server every 30 minutes,” OX Security researcher Moshe Siman Tov Bustan said. “The malware adds malicious capabilities by requesting consent for ‘anonymous, non-identifiable analytics data’ while actually exfiltrating complete conversation content from ChatGPT and DeepSeek sessions.”
The malicious browser add-ons have been found to impersonate a legitimate extension named “Chat with all AI models (Gemini, Claude, DeepSeek…) & AI Agents” from AITOPIA that has about 1 million users. They are still available for download from the Chrome Web Store as of writing, although “Chat GPT for Chrome with GPT-5, Claude Sonnet & DeepSeek AI” has since been stripped of its “Featured” badge.
Once installed, the rogue extensions request that users grant them permissions to collect anonymized browser behavior to purportedly improve the sidebar experience. Should the user agree to the practice, the embedded malware begins to harvest information about open browser tabs and chatbot conversation data.
To accomplish the latter, it looks for specific DOM elements inside the web page, extracts the chat messages, and stores them locally for subsequent exfiltration to remote servers (“chatsaigpt[.]com” or “deepaichats[.]com”).
What’s more, the threat actors have been found to leverage Lovable, an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered web development platform, to host their privacy policies and other infrastructure components (“chataigpt[.]pro” or “chatgptsidebar[.]pro”) in an attempt to obfuscate their actions.
The consequences of installing such add-ons can be severe, as they have the potential to exfiltrate a wide range of sensitive information, including data shared with chatbots like ChatGPT and DeepSeek, and web browsing activity, including search queries and internal corporate URLs.
“This data can be weaponized for corporate espionage, identity theft, targeted phishing campaigns, or sold on underground forums,” OX Security said. “Organizations whose employees installed these extensions may have unknowingly exposed intellectual property, customer data, and confidential business information.”
Legitimate Extensions Join Prompt Poaching
The disclosure comes as Secure Annex said it identified legitimate browser extensions such as Similarweb and Sensor Tower’s Stayfocusd – each with 1 million and 600,000 users, respectively – engaging in prompt poaching.
Similarweb is said to have introduced the ability to monitor conversations in May 2025, with a January 1, 2026, update adding a full terms of service pop-up that makes it explicit that data entered into AI tools is being collected to “provide the in-depth analysis of traffic and engagement metrics that you expect by using the Service.” A December 30, 2025, privacy policy update also spells this out –
This information includes prompts, queries, content, uploaded or attached files (e.g., images, videos, text, CSV files) and other inputs that you may enter or submit to certain artificial intelligence (AI) tools, as well as the results or other outputs (including any attached files included in such outputs) that you may receive from such AI tools (“AI Inputs and Outputs”).
Considering the nature and general scope of AI Inputs and Outputs and AI Metadata that is typical to AI tools, some Sensitive Data may be inadvertently collected or processed. However, the aim of the processing is not to collect Personal Data in order to be able to identify you. While we cannot guarantee that all Personal Data is removed, we do take steps, where possible, to remove or filter out identifiers that you may enter or submit to these AI tools.
Further analysis has revealed that Similarweb uses DOM scraping or hijacks native browser APIs like fetch() and XMLHttpRequest() – like in the case of Urban VPN Proxy – to gather the conversation data by loading a remote configuration file that includes custom parsing logic for ChatGPT, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, and Perplexity.
Secure Annex’s John Tuckner told The Hacker News that the behavior is common to both Chrome and Edge versions of the Similarweb extension. Similarweb’s Firefox add-on was last updated in 2019.
“It is clear prompt poaching has arrived to capture your most sensitive conversations and browser extensions are the exploit vector,” Tuckner said. “It is not clear if this violates Google’s policies that extensions should be built for a single purpose and not load code dynamically.”
“This is just the beginning of this trend. More firms will begin to realize these insights are profitable. Extension developers looking for a way to monetize will add sophisticated libraries like this one supplied by the marketing companies to their apps.”
Users who have installed these add-ons and are concerned about their privacy are advised to remove them from their browsers and refrain from installing extensions from unknown sources, even if they have the “Featured” tag on them.